Top 10 Aircraft Wire Types and Their Applications Explained
In the aerospace industry, the choice of aircraft wire is crucial for ensuring safety and reliability. Renowned expert, Dr. Mike Johnson, emphasizes, "The right wire can make all the difference in aircraft performance." With various wire types available, understanding their specific applications is vital.
Aircraft wire serves multiple functions, from powering avionics to connecting critical systems. Each wire type has unique characteristics. For example, some wires are designed for high-temperature environments, while others are built for flexibility and weight savings. An informed selection can prevent costly failures or malfunctions.
However, the landscape of aircraft wire is not without challenges. Understanding the nuances between wire types can be overwhelming. Additionally, advancements in materials often leave older designs underappreciated. It’s essential for industry professionals to stay updated on current trends and innovations to make informed choices. This exploration into the top 10 aircraft wire types reveals both the complexities and necessities for safe aviation practices.
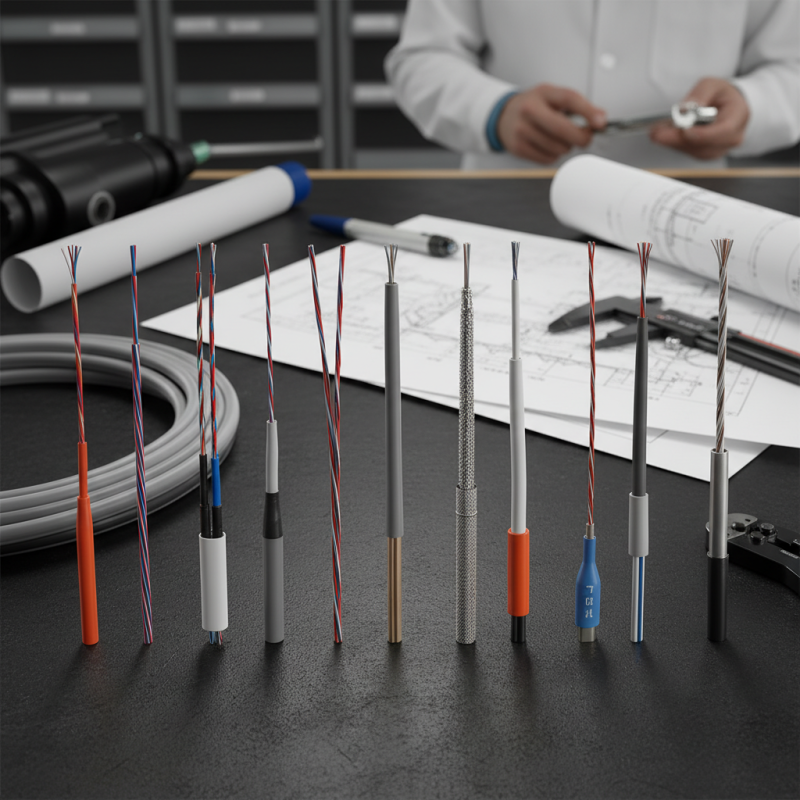

Types of Aircraft Wires: An Overview of Key Categories
Aircraft wires are crucial for reliable operations. They connect systems, transmit power, and ensure communication. Different types of wires suit various applications. Each category has unique characteristics that serve specific needs.
One key type is power wires. These are designed for high voltage and current. They must withstand harsh environments without degrading. Signal wires are another category. They carry low-level electrical signals for communication. Their insulation must protect against interference.
Aircraft also utilize shielded cables. These wires prevent electromagnetic interference. This is vital for maintaining safety and functionality. As technology evolves, so do wire types. Designers need to be mindful of choosing the right wire. It impacts performance and reliability. In some cases, the wrong choice can lead to failures. Every detail matters in aircraft wiring. Attention to these categories can enhance safety in aviation.
Top 10 Aircraft Wire Types and Their Applications
Application of Copper Wires in Aircraft Systems and Components
Copper wires play a crucial role in aircraft systems and components. They are widely used for power transmission due to their excellent conductivity. In avionics, copper wires connect instruments, gauges, and displays. Their reliability ensures pilots receive accurate information.
Copper wires are frequently found in heavy-duty applications. They are utilized in the aircraft's electrical distribution system. This allows for efficient energy transfer to various components. However, corrosion can be an issue over time. Regular inspections are necessary to maintain performance.
The weight of copper wires can be a disadvantage. Aircraft design often prioritizes lightweight materials. This conflict creates challenges for engineers. Often, they must balance conductivity, weight, and durability. Looking ahead, innovations in wire materials may offer solutions to these issues.
Understanding Aluminum Wire Usage in Aviation Circuitry
Aluminum wire is a common choice for aviation circuitry due to its lightweight properties. This material significantly reduces the overall weight of aircraft. According to a report by the Federal Aviation Administration, lightweight wiring can improve fuel efficiency by up to 2%. This reduction can translate into substantial cost savings over time.
Aluminum wire is not without its challenges. While it offers excellent conductivity, it is more prone to corrosion than copper. The aviation industry must address this issue to ensure reliability. Proper coating and insulation techniques are vital in enhancing the longevity of aluminum wires. Engineers often debate if aluminum is the best choice in all scenarios.
Moreover, the heat dissipation capabilities of aluminum fall short compared to other materials. In high-temperature environments, maintaining performance can be a struggle. This factor requires careful consideration in the design stage. A balance between weight savings and electrical performance must be achieved. Continued research and development are essential to refine aluminum's application in aviation circuitry.
Top 10 Aircraft Wire Types and Their Applications Explained
| Wire Type | Material | AWG Size | Purpose | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stranded Copper Wire | Copper | 20 - 10 AWG | Power Distribution | Control Systems |
| Aluminum Wire | Aluminum | 24 - 12 AWG | Signal Transmission | Lighting Systems |
| Teflon Insulated Wire | Copper | 22 - 16 AWG | High-Temperature Applications | Engine Wiring |
| Silicone Insulated Wire | Copper | 20 - 12 AWG | Flexible Applications | Movable Parts |
| Shielded Wire | Copper | 22 - 18 AWG | Interference Reduction | Data Transmission |
| High-Voltage Wire | Copper or Aluminum | 10 - 4 AWG | Power Systems | Electrical Equipment |
| Braid Wire | Copper or Aluminum | Various | Flexible Connections | Aircraft Components |
| Twisted Pair Wire | Copper | 24 - 22 AWG | Data Communication | Networking |
| Fiber Optic Cable | Glass/Fiber | N/A | High-Speed Data Transfer | Avionics Systems |
The Role of Fiber Optic Cables in Modern Aircraft Communications
Fiber optic cables play a crucial role in modern aircraft communications. They transmit data at high speeds over long distances. These cables are lightweight and flexible, making them ideal for aircraft. Their ability to resist electromagnetic interference is a significant advantage. This leads to clearer signals and fewer disruptions in communication systems.
In an age where data transfer is vital, the use of fiber optics has become essential. Aircraft can now support more complex systems with greater efficiency. However, not all aircraft utilize fiber optics yet. Some still rely on traditional wiring, which can limit performance. It raises questions about the reliance on outdated technologies.
Implementing fiber optics also comes with challenges. Installation can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge. Maintenance might pose difficulties as well. These issues provoke reflection on the balance between innovation and practicality. Embracing fiber optics fully could enhance operational capabilities significantly. Yet, caution must be applied to avoid potential pitfalls in integration.
Emerging Trends in Aircraft Wiring: Innovations and Future Directions
The aerospace industry is witnessing significant shifts in aircraft wiring technology. Recent reports indicate that wire weight reduction is a top priority. The global market for aircraft wiring is projected to reach $1.5 billion by 2025, driven by these innovations.
One trend is the adoption of lightweight materials. Composite and aluminum alloys are used to minimize weight while maintaining strength. This suggests that materials science remains pivotal in advancing wiring solutions. Additionally, advances in insulation technology, like lightweight fluoropolymers, offer improved heat resistance. This is crucial as more electrical systems are integrated into aircraft.
Emerging trends reveal challenges too. As aircraft systems become more complex, managing electromagnetic interference is a growing concern. Reports highlight that about 25% of aviation incidents relate to wiring issues. Innovations must address these vulnerabilities. The future design of aircraft wiring needs continuous improvements. The industry must remain vigilant, balancing innovation with safety.
Related Posts
-

2026 Top Airplane Wire Technologies Transforming Aviation Industry?
-

How to Choose the Best Cable Solutions for Your Home and Office Needs
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Cable Clamp for Your Project
-

How to Choose the Right Cable Clamp for Your Project Needs
-
How to Choose the Right Airplane Wire for Your Aviation Needs
-

What is cable wire and how is it used in various applications?
